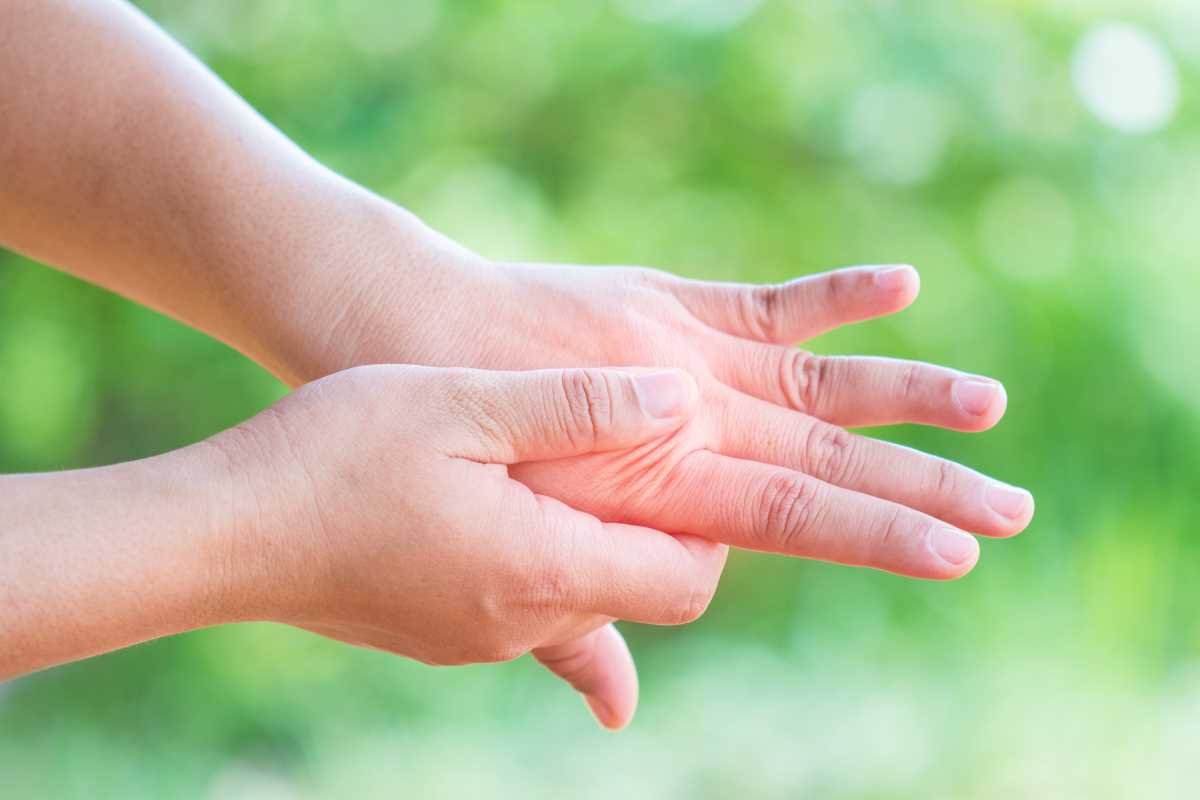
Maintaining joint health and flexibility can keep active individuals mobile and injury-free. Whether you’re a runner, cyclist, yogi, or weightlifter, repetitive joint stress from regular physical activity can often lead to stiffness, discomfort, or even long-term issues if not properly managed. One of the most powerful tools to support joint health comes in a small yet mighty package—omega-3 fatty acids.
Famous for their role in heart and brain health, omega-3s also reduce inflammation, protect joint cartilage, and enhance flexibility and mobility. Understanding how omega-3s work, where to find them, and how to incorporate them into your diet can be a game-changer for anyone with an active lifestyle.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats, meaning your body cannot produce them independently—you have to obtain them from food or supplements. The three primary types of omega-3s are:
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid): Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, EPA supports joint health by reducing inflammatory markers that can contribute to pain and arthritis.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid): Besides playing a crucial role in brain health, DHA also contributes to joint lubrication and flexibility.
- ALA (Alpha-linolenic acid): This plant-based omega-3 converts in small amounts to EPA and DHA, though not as efficiently. ALA still offers significant benefits, particularly for those following plant-based diets.
How Omega-3s Support Joint Health and Flexibility
Maintaining joint health and flexibility is crucial for those living an active lifestyle, and omega-3 fatty acids can be a powerful ally in this pursuit. Renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties, these essential fats help reduce swelling and discomfort and play a key role in protecting joint cartilage and improving mobility. Let's explore how omega-3s work to keep your joints strong, flexible, and ready for action.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Inflammation is a natural response to physical activity, especially intense or repetitive exercise like weightlifting or running. While short-term inflammation can help repair tissues, chronic inflammation might lead to joint pain or arthritis over time.
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA, directly combat inflammation by reducing the production of inflammatory molecules such as cytokines and prostaglandins. Studies show that individuals supplementing with omega-3s experience significant reductions in joint pain and stiffness compared to those who do not, particularly in cases of osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
2. Cartilage Protection
Cartilage is the rubbery tissue that cushions your joints, preventing bones from rubbing together during movement. Overuse injuries, age, or diseases like arthritis can wear down cartilage, leading to painful stiffness. Omega-3 fatty acids help reduce enzymes that break down cartilage, thereby preserving joint integrity.
3. Improved Joint Lubrication and Mobility
Maintaining flexible joints is key to performing dynamic movements, whether you’re stretching in yoga or powering through squats at the gym. Omega-3s increase the fluidity of cell membranes, which can enhance joint lubrication. This can reduce friction during movement, keeping active individuals agile and even preventing injuries caused by stiff or poorly lubricated joints.
4. Reducing Morning Stiffness
For many people—athletes and non-athletes alike—stiffness is most noticeable after a night's rest. Omega-3 fatty acids are shown to improve morning stiffness significantly, an effect that’s especially beneficial for those with arthritis or undergoing recovery from intensive training.
5. Better Recovery from Joint Injuries
Omega-3s may also speed up recovery after joint injuries. Their anti-inflammatory and healing properties can reduce swelling and encourage tissue repair, making them an excellent addition during recovery phases.
Best Sources of Omega-3s
Adding omega-3s to your diet doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some top sources to consider, whether you prefer animal-based or plant-based options.
1. Fish and Fish Oil
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are among the best dietary sources of omega-3s, rich in both EPA and DHA. Fish oil supplements are a convenient alternative for those who don’t eat fish regularly, and they’ve been extensively studied for joint health benefits.
How to Incorporate:
- Enjoy grilled salmon with a side of vegetables for dinner.
- Add canned sardines to salads or sandwiches.
- Take high-quality fish oil capsules daily as a supplement.
2. Algae-Based Omega-3 Supplements
For vegans or vegetarians, algae-based omega-3 supplements are an excellent source of DHA and EPA. Algae supplements are particularly sustainable and provide the same anti-inflammatory benefits as fish oil without relying on seafood.
How to Incorporate:
- Choose an algae-based omega-3 capsule as part of your morning routine.
- Look for fortified plant-based foods that contain algae-derived omega-3s.
3. Flaxseeds and Flaxseed Oil
Flaxseeds are one of the richest plant-based sources of ALA. While ALA doesn’t convert as efficiently to DHA and EPA, it still contributes to overall omega-3 intake and has other health benefits.
How to Incorporate:
- Sprinkle ground flaxseeds over oatmeal, smoothies, or salads.
- Use flaxseed oil as a topping for roasted vegetables or in salad dressings (don’t cook with it, as heat damages its nutritional value).
4. Chia Seeds
Similar to flaxseeds, chia seeds are another excellent plant-based source of ALA. They are versatile and easy to add to a variety of dishes.
How to Incorporate:
- Stir chia seeds into a smoothie or overnight oats.
- Make a chia seed pudding with almond milk and a touch of maple syrup.
5. Walnuts
Walnuts are a simple snack option that pack a hefty dose of ALA.
How to Incorporate:
- Snack on a handful of walnuts after a workout.
- Add walnuts to baked goods or chop them into a salad for crunch.
6. Hemp Seeds
Rich in ALA, hemp seeds are another potent plant-based source of omega-3s.
How to Incorporate:
- Blend hemp seeds into protein shakes or smoothies.
- Sprinkle them over avocado toast for extra nutrients.
Tips for Omega-3 Intake
For active individuals aiming to optimize joint health, here are some tips to help you get the most out of omega-3 fats:
- Set a Schedule: Consistency is key. Aim for a daily intake of omega-3s, whether through food or supplements.
- Balance Your Fats: Reduce consumption of omega-6 fatty acids (found in processed foods) to maintain a healthy omega-3 to omega-6 ratio.
- Pair with Exercise Recovery Foods: Combine omega-3-rich foods with antioxidants and protein for post-workout recovery.
For active people who put regular stress on their joints, omega-3 fatty acids are an essential ally in maintaining flexibility, reducing inflammation, and supporting overall joint health. From fatty fish and algae supplements to plant-based sources like flaxseeds and walnuts, there’s an option for everyone to reap the benefits.
Incorporating omega-3s into your daily diet can protect your joints, enhance mobility, and stay ready for whatever physical challenges lie ahead. A little extra attention to your nutrition today can improve performance and long-term joint health tomorrow.
 (Image via
(Image via





.jpg)